Product Description
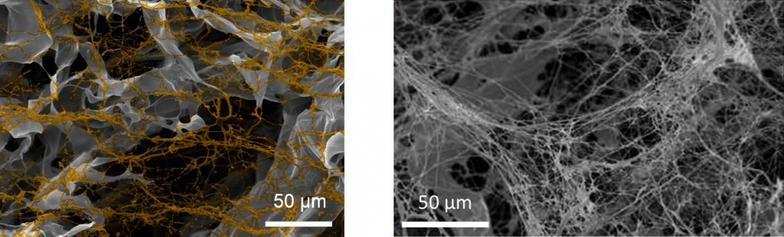
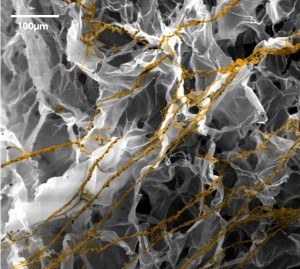
BioMIMESYS® is an organ-specific Extracellular Matrix (ECM) formed by the crosslinking reaction of hydrosoluble modified hyaluronic acid (HA) and other ECM components (collagens, fibronectin, etc.) with ADH (Adipic acid dihydrazide), to create a "Hydroscaffold" 3D cell culture system.
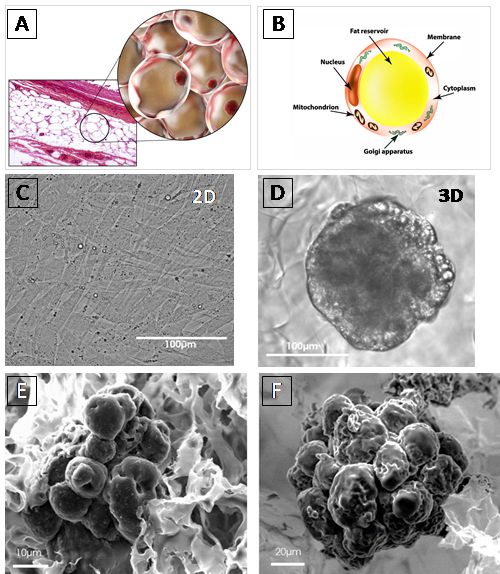
BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue represents a new generation of mimetic hydroscaffold for 3D adipocyte and adipocyte-like cell cultures. Available in a ready-to-use format, it enables the culture of adipocytes and adipocyte-like cells under physiological conditions that are representative of the microenvironment found in adipose tissue. The highly porous nature of the scaffold allows the rapid uptake of nutrients, oxygen, etc. into the cells to create a reproducible study model for all downstream analyses used with 3D adipocytes culture.
BIOMIMESYS® Adipose Tissue is easy & ready-to-use. Upon receiving the vacuum sealed 96-well plate open it (under a hood) and add the cells directly on top of the matrix. Changing the culture medium is easy as well. To remove medium, simply draw the medium with a pipette between the matrix and the edge of the well. To refresh the medium, place fresh medium onto the surface of the matrix.
•Hyaluronic acid (HA) + Collagen I & VI system, is a major component of the adipocyte extracellular matrix (ECM), where it plays an important role in connective tissue.
•HA-based scaffolds are formed by HA-grafted RGDS + Collagen I & VI system crosslinking HA with ADH to form reticulated chains.
•High molecular weight HA is made from Gram+bacteria, which makes it easily reproducible.
•PHYSICOCHEMICAL FEATURES
> Porosity: 120 ± 50μm
> Rheology: Young’s modulus: E= 0.45 ± 0.05kPa
> Swelling ratio = 60 ± 10g/g
| Cell Lines | |
| Human breast adenocarcinoma | MCF-7 |
| Human breast carcinoma | CAL-51 / T-47D / MDAMB-231 / MCF10A |
| Normal mouse preadipocytes | 3T3-L1 / 3T3-F442A |
| Human colorectal adenocarcinoma | HCT 116 |
| Normal human Keratinocytes | HaCaT |
| Normal human Fibroblasts | BJ |
| Primary Cells | |
| Human white pre-adipocyte subcutaneous | HWP cryopreserved / HPrAD |
| Human Fibroblasts | NHDF |
| Human Keratinocytes | NHEK |
| Stem Cells | |
| Human induced pluripotent stem cells | hiPS |
| Human sebocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells | PCi-SEB |
1. Louis, F. et al. A biomimetic hydrogel functionalized with adipose ECM components as a microenvironment for the 3D culture of human and murine adipocytes. Biotechnol Bioeng 114, 1813–1824 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26306
2. Neels, J. G., Thinnes, T. & Loskutoff, D. J. Angiogenesis in an in vivo model of adipose tissue development. FASEB J 18, 983–985 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-1101fje
3. Cristancho, A. G. & Lazar, M. A. Forming functional fat: a growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12, 722–734 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3198
4. Dalby, M. J., Gadegaard, N. & Oreffo, R. O. C. Harnessing nanotopography and integrin-matrix interactions to influence stem cell fate. Nat Mater 13, 558–569 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3980
5. McBeath, R., Pirone, D. M., Nelson, C. M., Bhadriraju, K. & Chen, C. S. Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev Cell 6, 483–495 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1534-5807(04)00075-9
6. Wang, L., Johnson, J. A., Zhang, Q. & Beahm, E. K. Combining decellularized human adipose tissue extracellular matrix and adipose-derived stem cells for adipose tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 9, 8921–8931 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2013.06.035
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY, NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES.
Manufactured by : HCS Pharma
| Questions about this product? Email us at orders@iwai-chem.com or give us a call: (650) 486-1541 |






